The Public Provident Fund (PPF) is one of the most trusted long-term savings schemes in India, backed by the Government of India. It is designed for people who want safe returns, disciplined savings, and tax benefits all in one investment. PPF is especially popular among salaried individuals, self-employed professionals, and long-term investors who prefer stability over risk.
A PPF account allows you to invest a small or large amount every year and earn interest at a rate announced by the government each quarter. The scheme comes with a 15-year lock-in period, which encourages long-term wealth creation while protecting your money from market volatility. One of the biggest attractions of PPF is its EEE tax status, meaning your investment, interest earned, and maturity amount are all tax-free.
In this article, you’ll learn what PPF is, how it works, the current interest rate structure, key benefits, and why it remains one of the best long-term investment options in India.
What Is Public Provident Fund (PPF)?
The Public Provident Fund (PPF) is a voluntary, long-term savings and investment scheme backed by the Government of India. It was originally introduced in 1968 and continues to be one of the core small savings instruments available to Indian residents.
PPF combines the benefits of guaranteed returns, tax savings, and compound interest growth, making it a go-to option for conservative investors who want to build a secure retirement corpus or save for long-term goals without exposure to market risk. The scheme is managed by the government, and accounts can be opened at authorized banks or post offices.
How Does PPF Work? Step-by-Step Process Explained
Here’s how a PPF account works:
- Open a PPF Account: You can open a PPF account at a nationalized bank, a post office, or through many private bank net-banking portals.
- Make Contributions: You must deposit a minimum of ₹500 per year and can deposit up to ₹1.5 lakh per financial year (basis for earning interest).
- Interest Is Credited Annually: The interest rate is decided by the government and credited once a year (typically on March 31).
- Compounding: Interest is compounded yearly, helping grow your savings over time.
- Maturity After 15 Years: The account matures after 15 years, though you can choose to extend it in 5-year blocks.
This simple process makes PPF predictable and easy to use for investors who prefer safe, long-term growth.
PPF Interest Rate in India: How It Is Calculated
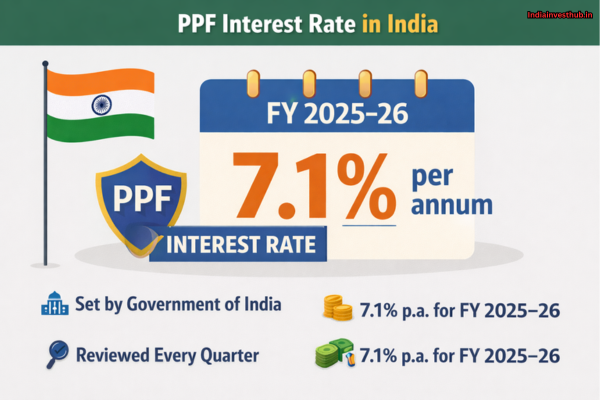
The PPF interest rate is set by the central government and reviewed every quarter in consultation with the Ministry of Finance. For the FY 2025–26, the PPF interest rate is 7.1% per annum.
Interest is calculated on the lowest balance between the 5th day and the last day of each month, and the total is credited at the end of the financial year. This annual compounding makes PPF a powerful tool for long-term savings.
PPF Account Eligibility: Who Can Open a PPF Account?
A PPF account can be opened by:
- Indian residents (adults)
- Parents/guardians on behalf of minor children
- Individuals with a valid PAN and KYC documents
Non-Resident Indians (NRIs) generally cannot open a new PPF account, though existing accounts opened while they were residents can usually be continued until maturity.
PPF Investment Limits: Minimum, Maximum, and Lock-In Period
PPF has well-defined investment rules:
- Minimum yearly deposit: ₹500
- Maximum yearly deposit: ₹1.5 lakh (no interest is earned on contributions above this limit)
- Lock-in period: 15 years (extendable in 5-year blocks after maturity)
These limits help ensure disciplined long-term investing without risking capital.
Key Benefits of PPF: Safety, Tax Savings, and Guaranteed Returns
Public Provident Fund comes with three major benefits:
1) Government-Backed Safety
PPF investments are backed by the Government of India, meaning your principal and returns are secure with no market risk.
2) Tax Benefits (EEE Status)
PPF follows the EEE (Exempt-Exempt-Exempt) tax regime:
- Contributions are tax-deductible under Section 80C (up to ₹1.5 lakh per year)
- Interest earned is tax-free
- Maturity proceeds are tax-free
3) Guaranteed Returns
With no dependency on market performance, PPF offers a fixed return, making it perfect for risk-averse long-term investors.
PPF vs FD vs RD vs ELSS: Which Is Better for Long-Term Savings?
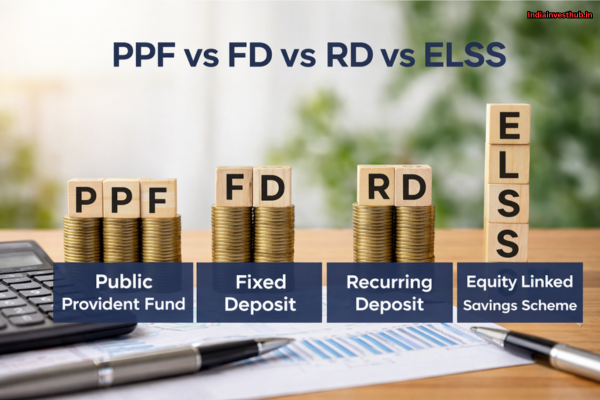
Comparing PPF with other safe instruments helps investors understand where it fits:
- FD (Fixed Deposit): Offers guaranteed returns but interest is taxable unless it’s a tax-saving FD, and liquidity is generally higher.
- RD (Recurring Deposit): Good for disciplined monthly savings, but also taxable and lacks long-term compounding power.
- ELSS (Equity Linked Savings Scheme): Offers equity exposure with higher returns potential but also higher risk and shorter lock-in.
For long-term, tax-free wealth building, PPF often suits conservative goals like retirement planning or education funding.
PPF Tax Benefits Explained:
Under Indian tax law:
- Contributions to PPF qualify for deduction under Section 80C (up to ₹1.5 lakh).
- Interest earned and maturity amount are entirely tax-exempt.
- This triple tax benefit makes PPF especially attractive compared to taxable fixed-income instruments.
Partial Withdrawal and Loan Rules in PPF Account:
PPF allows limited flexibility even with its long lock-in:
- Partial withdrawals are permitted from the 7th financial year onward, subject to conditions.
- Loans can be taken against the PPF balance from the 3rd to 6th year, which must be repaid within a specified period.
- Premature closure is allowed in extreme circumstances (such as higher education or medical needs) but usually comes with a penalty and reduced interest.
How to Open a PPF Account Online or Offline (Bank & Post Office):

Opening a PPF account is straightforward:
- Approach a post office or authorized bank branch.
- Fill out required forms and submit KYC documents (PAN, address proof, photo).
- Make your initial deposit (minimum ₹500 per year).
- You’ll receive a passbook or account details.
Many banks now allow online PPF account opening and management through net-banking or mobile apps.
FAQs – Public Provident Fund
Q1: What is the minimum amount to invest in PPF?
👉The minimum yearly deposit is ₹500.
Q2: How long is the lock-in period for PPF?
👉PPF has a 15-year lock-in period, extendable in 5-year blocks.
Q3: Can NRIs open a PPF account?
👉NRIs generally cannot open new PPF accounts, but existing accounts can continue until maturity.
Q4: Is the interest rate fixed forever?
👉No, the government reviews PPF rates every quarter.
Q5: Is interest earned on PPF taxable?
👉No—interest and maturity proceeds are fully tax-exempt.
Conclusion:
The Public Provident Fund remains one of the most reliable and tax-efficient savings instruments for Indian investors focused on long-term goals and retirement planning. With its government guarantee, stable interest rate (currently around 7.1% p.a.), and triple tax benefits, PPF combines safety and growth in a way few other fixed-income options can match. Its rigid 15-year lock-in may not suit everyone, but for investors willing to commit to disciplined, long-term savings, PPF offers unmatched peace of mind and wealth accumulation potential.
So, are you ready to use PPF as a cornerstone of your long-term investment strategy?