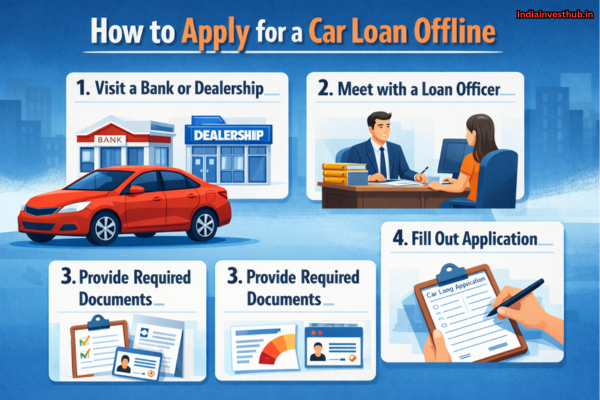
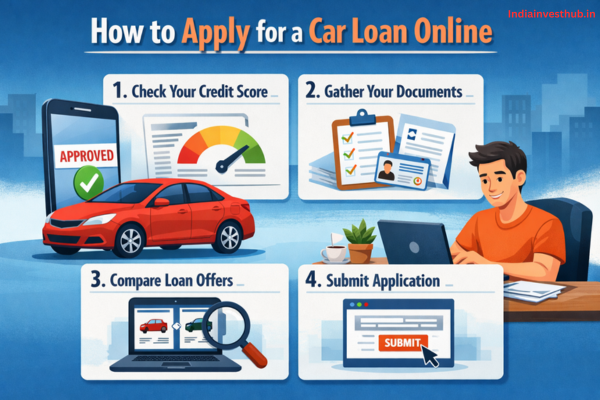
A car loan is a popular financing option that helps you buy a new or used car without paying the full amount upfront. Instead of using all your savings at once, a bank or financial institution pays for the car on your behalf, and you repay the amount in monthly instalments (EMIs) over a fixed period. Car loans make vehicle ownership easier and more affordable, especially for first-time buyers.
One of the main factors to consider while taking a car loan is the interest rate, which determines how much extra you pay over the loan amount. Interest rates vary based on the lender, loan tenure, your income, and your credit score. Eligibility criteria such as age, employment status, and monthly income also play a key role in loan approval.
In this article, you’ll clearly understand what a car loan is, how it works, how EMI is calculated, current interest rate factors, and who is eligible to apply. Whether you’re planning to buy a new car or a used one, this guide will help you make an informed and confident decision before taking a car loan.
What Is a Car Loan?
A Car Loan is a type of secured loan taken specifically to purchase a car. As a secured loan, the car itself is used as collateral: if you fail to repay, the lender has the right to repossess the vehicle. Car loans are offered by banks, non-banking financial companies (NBFCs), credit unions, and even some manufacturers’ finance arms. The amount you can borrow usually depends on factors such as your income, credit score, age, and the value of the car. Generally, lenders finance between 80%–100% of the car’s on-road price, with the borrower covering the balance as down payment.
Car loans are popular because they allow buyers to own a vehicle immediately while paying over several years. Instead of saving for years to buy a car outright, a buyer can leverage credit and start building utility from the car while repaying the loan gradually.
The Art of Financial Balance: Differentiating Between Needs and Wants
How Does a Car Loan Work? Step-by-Step Process
Understanding how a Car Loan works helps you plan repayments and financial commitments:
- Loan Application:
You complete a loan application with your chosen lender. This can be done online or at a branch. - Document Submission:
You submit required documentation (identity proof, income proof, address proof, bank statements, etc.) as part of your loan application. - Credit Evaluation:
The lender assesses your creditworthiness, income stability, and ability to repay. A strong credit score often leads to better interest rates. - Loan Offer and Approval:
Once evaluated, the lender approves a loan amount and terms, including interest rate, tenure, and EMI structure. - Disbursement:
Upon acceptance, the loan amount is disbursed—sometimes directly to the car dealer. - EMI Payments:
You begin monthly EMI payments, which include principal and interest, as agreed in the loan contract.
This structured mechanism allows purchasers to manage cash flow effectively while acquiring a depreciating asset.
Car Loan Interest Rates in India: How They Are Decided

Interest rates on a Car Loan are a crucial factor since they determine how much you will pay over the life of the loan. In India, car loan interest rates typically vary between 8% and 14% per annum, depending on the lender, borrower profile, credit score, and economic conditions.
Several factors influence car loan interest rates:
- Repo Rate and Macro Trends:
The Reserve Bank of India’s policy rates influence lending rates across the economy. When rates rise, car loan interest rates usually follow. - Credit Score:
A higher credit score (e.g., good CIBIL score) signals lower risk and often earns you a lower interest rate. - Loan Amount and Tenure:
Some lenders charge slightly higher rates for longer tenures or larger loan amounts. - Borrower’s Income and Stability:
Higher and steady income increases repayment capacity, lowering perceived risk and potentially lowering interest rates.
Since car loans are secured, interest rates can be lower compared to unsecured loans like personal loans.
Car Loan Eligibility Criteria: Age, Income, Credit Score
Before approving a Car Loan, lenders evaluate several eligibility criteria:
Age:
Most lenders require applicants to be between 21 and 65 years old, though some offer loans for slightly younger or older borrowers.
Income:
A stable and sufficient income is necessary to prove you can repay the EMIs. Salaried individuals often need to meet minimum salary thresholds set by the bank or NBFC.
Credit Score:
A strong credit score (e.g., 750 or higher on CIBIL) enhances eligibility and helps secure lower interest rates.
Employment History:
Steady employment history reassures lenders of repayment capacity.
These criteria ensure that lenders manage risk while offering credit that borrowers can realistically repay.
Documents Required for Car Loan Approval:

To secure a Car Loan, you typically need:
- Proof of Identity: Passport, Aadhaar, PAN, driver’s license, etc.
- Proof of Address: Utility bills, rental agreement, passport, etc.
- Proof of Income: Salary slips, bank statements, IT returns, etc.
- Photographs: Passport-size photos
- Vehicle Documents: Quotation from dealer, vehicle details
Providing accurate documentation speeds up the loan approval process and reduces the risk of rejection.
How to Calculate Car Loan EMI? EMI Formula and Examples
An EMI (Equated Monthly Instalment) is the fixed amount you pay every month until your car loan is repaid. The EMI consists of two parts—principal and interest.
The standard formula to calculate EMI is:
EMI = [P × R × (1+R)^N]/[(1+R)^N-1]
Where:
P = Principal loan amount
R = Monthly interest rate (annual rate/12/100)
N = Loan tenure in months
Example:
If you borrow ₹10,00,000 at an annual interest rate of 10% for 5 years (60 months), the monthly EMI would be around ₹21,247.
Most lenders provide online EMI calculators to help you plan your budget before applying for a car loan.
Car Loan Tenure Options: Short-Term vs Long-Term Loan
Choosing the right loan tenure impacts your monthly EMIs and total interest paid.
Short-Term Car Loan (1–3 years)
- Higher EMI
- Less interest paid overall
- Suitable if you want to be debt-free sooner
Long-Term Car Loan (4–7 years)
- Lower monthly EMI
- More interest paid total
- Better if you want manageable monthly cash flow
Many buyers prioritize cash flow and opt for longer tenure, especially when balancing household expenses, but longer tenures increase total cost due to interest.
New Car Loan vs Used Car Loan: Key Differences

When choosing between financing a new or used car with a Car Loan, there are some differences:
Factor | New Car Loan | Used Car Loan |
|---|---|---|
Interest Rate | Lower interest rates (generally 8%–10%) | Higher interest rates (usually 11%–16%) |
Loan Amount | Up to 90%–100% of on-road price | Usually 60%–80% of car value |
Loan Tenure | Longer tenure (up to 7 years) | Shorter tenure (up to 5 years) |
Eligibility Criteria | Easier approval with moderate credit score | Stricter credit and income checks |
Down Payment | Lower down payment required | Higher down payment required |
Processing Fees | Lower or sometimes waived | Higher processing charges |
Car Age Limit | Not applicable (brand-new vehicle) | Car age usually limited to 3–5 years |
Resale Value | Higher resale value | Lower resale value |
Risk for Lender | Lower risk due to new vehicle | Higher risk due to depreciation |
Best For | Buyers wanting lower EMI and better terms | Buyers looking for budget-friendly cars |
Benefits and Drawbacks of Taking a Car Loan:
Like any financial product, a Car Loan has pros and cons:
Benefits:
- Immediate ownership of the car
- Convenient payment through EMIs
- Potential tax benefits (for business use)
- Helps maintain liquidity, especially if you prefer investing surplus funds elsewhere
Drawbacks:
- Interest adds to total cost
- Default risks include repossession
- Longer tenure increases total interest paid
Understanding these helps you make balanced decisions based on your financial goals.
FAQs – Car Loan
Q1: Can I prepay a car loan?
👉Yes, most lenders allow part or full prepayment with or without a small charge.
Q2: Is a co-applicant beneficial?
👉Adding a co-applicant with strong credit increases approval chances and may lower interest.
Q3: Can I transfer my car loan to another lender?
👉Yes, through balance transfer options if better rates are available.
Q4: Does car loan interest vary for used cars?
👉Yes, used car loans typically carry higher interest rates.
Q5: How soon should I check my credit score before applying?
👉Ideally at least a month before applying to improve it if low.
Conclusion:
A Car Loan is more than just a borrowing tool—it’s a financial strategy that enables you to acquire a depreciating asset without tying up all your capital upfront. Whether you’re a first-time buyer or seasoned investor analyzing credit products, knowing how car loan interest rates work, what lenders look for in eligibility, how EMIs are calculated, and the differences between new and used car loans helps you make sound decisions. While the convenience and liquidity management of a car loan are appealing, investors must balance it with interest costs and repayment capacity before signing on the dotted line.
So before you apply for a car loan, consider this question—have you evaluated both your short-term cash flow and long-term financial goals to decide if this loan truly aligns with your investment strategy?