A Recurring Deposit (RD) is a simple and disciplined way to save money regularly without taking any market risk. It is especially popular among salaried individuals, students, and first-time investors who want to build savings gradually. In an RD, you deposit a fixed amount every month for a chosen period, and the bank or post office pays interest on the total amount at the end of the tenure. Since the investment is done monthly, RD makes saving easy and affordable, even with small amounts.
One of the biggest advantages of an RD is that it helps develop a strong saving habit while offering better returns than a regular savings account. RD interest rates are usually similar to Fixed Deposit (FD) rates and depend on the tenure and the financial institution. You can choose flexible tenures ranging from 6 months to 10 years, making RD suitable for short-term and long-term goals like buying a gadget, planning a vacation, or creating an emergency fund.
In this article, you’ll clearly understand what RD (Recurring Deposit) is, how it works step-by-step, its key benefits, current interest rate factors, and how to open an RD account easily online or offline in India.
What Is RD (Recurring Deposit)?
Recurring Deposit (RD) is a savings and investment option where you deposit a fixed amount every month for a fixed period at a predetermined interest rate. At the end of the tenure, you receive the total amount deposited plus interest.
RD is ideal for people who:
- Earn monthly income
- Want disciplined savings
- Prefer low risk
- Don’t have a lump sum to invest at once
Unlike FD, where you invest a lump sum, RD helps you build wealth gradually.
How Does a Recurring Deposit Work? Step-by-Step Explanation
Recurring Deposit works in a very structured way:
- Choose a monthly deposit amount
Example: ₹500, ₹1,000, ₹5,000 per month - Select the RD tenure
Common tenures range from 6 months to 10 years, depending on the bank or post office. - Interest rate is fixed at the start
The interest rate remains the same throughout the RD tenure. - Monthly deposits continue automatically
Most banks auto-debit the RD amount from your savings account. - Interest is compounded
Interest is usually compounded quarterly, similar to FD. - Maturity payout
At the end of the RD tenure, you receive the total savings + interest.
This step-by-step structure makes RD simple and stress-free.
RD Interest Rates in India – How They Are Calculated
Recurring Deposit interest rates are decided by:
- RBI monetary policy trends
- Bank liquidity needs
- RD tenure length
- Customer category (regular or senior citizen)
RD interest rates are usually similar to FD rates of the same tenure. Many public and private banks revise RD rates periodically. Senior citizens often receive an additional interest benefit.
Interest in RD is calculated using compound interest, which means earlier deposits earn interest for a longer time compared to later ones.
Types of RD Accounts (Bank RD, Post Office RD, Corporate RD):
Recurring Deposit options in India generally fall into three categories:
1) Bank RD
Offered by public and private banks like SBI, HDFC, ICICI, Axis, etc.
Most popular and easy to manage online.
2) Post Office RD
Backed by the Government of India.
Known for safety and stability.
Post Office RD usually comes with a standard 5-year tenure and fixed interest rate.
3) Corporate / NBFC RD
Offered by companies or NBFCs.
Often offer higher interest, but risk is slightly higher than bank or post office RD.
For conservative investors, bank RD and post office RD are usually preferred.
RD vs FD vs Savings Account – Which Is Better for Monthly Savings?
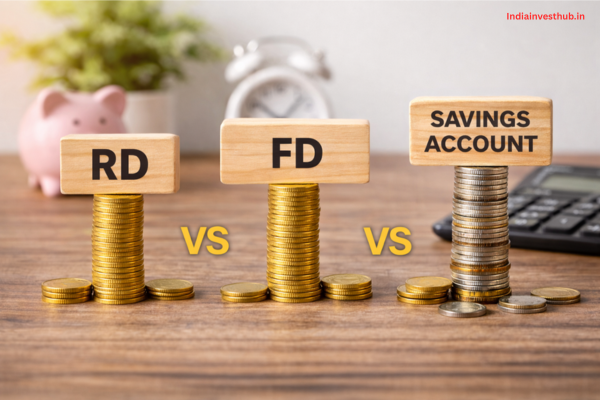

Recurring Deposit is best compared with FD and savings accounts:
Savings Account
- High liquidity
- Low interest
- No discipline enforced
Fixed Deposit (FD)
- Lump sum investment
- Higher interest
- Not ideal for monthly savers
Recurring Deposit (RD)
- Monthly savings habit
- Better interest than savings account
- Perfect for salaried individuals
If your goal is monthly disciplined saving, RD fits better than FD or savings accounts.
Key Benefits of Recurring Deposit (RD) for Salaried Individuals:
Recurring Deposit offers several advantages, especially for people with fixed monthly income:
(i) Encourages regular savings
(ii) Low minimum investment (often starting from ₹500/month)
(iii) Fixed returns with low risk
(iv) Predictable maturity amount
(v) Easy auto-debit facility
(vi) Suitable for short-term and medium-term goals
This is why RD is commonly used for goals like vacations, gadgets, emergency funds, or education expenses.
RD Tenure Options – Short-Term vs Long-Term RD
Recurring Deposit tenure can be chosen based on your goal:
Short-Term RD (6 months to 1 year)
- Emergency fund building
- Short-term expenses
- Parking surplus cash
Medium-Term RD (2–3 years)
- Travel planning
- Marriage or event expenses
- Education-related costs
Long-Term RD (5 years or more)
- Wealth discipline
- First-time investing habit
- Gradual corpus building
Choosing the right tenure helps align RD with your financial goals.
RD Taxation Rules – Is RD Interest Taxable?
Recurring Deposit interest is taxable in India.
Key points:
- RD interest is added to your total income
- Taxed as per your income slab
- Banks may deduct TDS if interest crosses the applicable threshold
If your total income is below the taxable limit, you can submit Form 15G (non-senior citizens) or Form 15H (senior citizens) to avoid TDS deduction.
Unlike 5-year tax-saving FD, RD does not offer Section 80C tax deduction.
RD for Students, Housewives, and First-Time Investors:
Recurring Deposit is one of the best entry-level investment tools.
For students
- Builds savings habit early
- Small monthly deposits
- Useful for future education or personal goals
For housewives
- Helps save household surplus
- No market risk
- Easy to manage
For first-time investors
- Simple and predictable
- No market knowledge required
- Builds confidence before moving to advanced investments
RD is often the first step in a person’s investment journey.
How to Open an RD Account Online or Offline in India:
Recurring Deposit can be opened easily:
Online Method
- Log in to your bank’s net banking or mobile app
- Select “Open RD”
- Choose monthly amount and tenure
- Confirm auto-debit
- RD account is created instantly
Offline Method
- Visit bank branch or post office
- Fill RD application form
- Submit KYC documents
- Start monthly deposits
Online RD opening is faster and more convenient today.
FAQs – Recurring Deposit
Q1: Is Recurring Deposit safe?
👉Yes, RD is considered a low-risk and safe investment, especially when opened with banks or post offices.
Q2: Can I stop RD before maturity?
👉Yes, premature closure is allowed, but interest may be reduced or penalized.
Q3: What happens if I miss an RD installment?
👉Banks may charge a small penalty, but your RD usually continues.
Q4: Is RD better than FD?
👉RD is better for monthly savings, while FD is better for lump sum investment.
Q5: Is RD interest taxable?
👉Yes, RD interest is taxable as per your income tax slab.
Conclusion:
Recurring Deposit is one of the simplest and most effective ways to build a saving habit while earning stable returns without taking market risk. It suits salaried individuals, students, and first-time investors who want structure, safety, and predictable growth. While it may not beat high-risk investments in returns, it plays a crucial role in disciplined wealth building.
So before choosing your next investment, ask yourself—do you want a safe monthly saving tool that quietly builds your future, or are you willing to accept higher risk for potentially higher returns?