A Fixed Deposit (FD) is one of the most popular and safest investment options in India, especially for people who want guaranteed returns without taking market risk. Simply put, when you open an FD, you deposit a lump sum amount in a bank or financial institution for a fixed time period, and in return, you earn interest at a pre-decided rate. Unlike stocks or mutual funds, FD returns do not depend on market ups and downs, which is why it’s trusted by beginners, working professionals, and senior citizens.
Many people choose FDs for goals like building emergency savings, saving for a child’s education, planning a vacation, or securing steady income after retirement. Another reason FDs remain a favorite is because they offer flexible tenure options—from a few days to several years—along with monthly, quarterly, or yearly interest payouts.
In this article, you will clearly understand what FD (Fixed Deposit) is, how it works step-by-step, the benefits of investing in FD, the latest interest rate factors, and how you can open an FD easily online or offline. If you want safe and stable growth for your money, FD can be a smart choice.
What Is FD (Fixed Deposit)?
FD (Fixed Deposit) is an investment where you deposit a lump sum amount in a bank, post office, or NBFC for a chosen time period (tenure) at a fixed interest rate. At maturity, you get back your principal + interest.
FD is called “fixed” because:
- Your interest rate is locked at the time of booking
- Your tenure is fixed (example: 6 months, 1 year, 5 years)
- Your returns are predictable
FD is best for people who want guaranteed returns instead of taking market risks.
The Art of Financial Balance: Differentiating Between Needs and Wants
How Does a Fixed Deposit Work? Step-by-Step Process
FD works in a very simple way:
- Choose the deposit amount
Example: ₹10,000, ₹1,00,000, ₹5,00,000 - Select the FD tenure
You can choose short-term or long-term options like 7 days, 1 year, 3 years, 5 years, etc. - Get a fixed interest rate
The bank offers an interest rate based on the tenure and your category (regular/senior citizen). - Interest gets added
Depending on the FD type, interest may be compounded quarterly and paid at maturity, or paid monthly. - Maturity payout
At the end of the FD, you receive the full maturity amount.
That’s why FD is considered a simple, low-risk product for investors who want stability.
Types of Fixed Deposits in India (Bank FD, Post Office FD, Corporate FD)
FD in India generally comes in three major types:
1) Bank FD
Offered by public and private banks (SBI, HDFC, ICICI, Axis, etc.).
Most trusted and widely used.
2) Post Office FD (Post Office Time Deposit)
Offered by India Post and backed by Government of India.
Post Office FD rates (as per recent updates) range around 6.90% to 7.50%, depending on tenure.
3) Corporate FD (Company FD / NBFC FD)
Offered by NBFCs and companies.
Usually offers higher rates, but risk can be higher than banks.
For safe investors, bank FD and post office FD are usually the top choices.
FD Interest Rates: How They Are Decided
FD interest rates are not random. They depend on:
- RBI repo rate and overall interest rate environment
- Bank’s need for deposits (liquidity requirement)
- FD tenure (longer tenures may offer slightly higher rates)
- Market competition among banks and small finance banks
In some periods, senior citizens can get FD rates close to 8% for 5-year deposits depending on the bank category and scheme availability.
✅ Key tip: FD rates change regularly, but once you book an FD, your rate remains locked until maturity.
FD Tenure Options: Short-Term vs Long-Term FD—Which Is Better?

FD tenure depends on your goal.
Short-Term FD (7 days to 1 year)
Best when:
- You need money soon
- You want safe parking for emergency funds
- You expect interest rates to rise soon (so you don’t want to lock long)
Long-Term FD (2 years to 5 years+)
Best when:
- You want predictable long-term returns
- You’re planning for future expenses (education, wedding, retirement)
- You want tax-saving FD (5-year lock-in)
Many investors use a “ladder strategy”: split money into multiple FDs of different tenures so liquidity stays smooth.
Key Benefits of Fixed Deposit (FD) for Safe Investors
FD is loved for solid reasons:
✅ Capital protection
Your principal amount stays safe (especially in bank/post office FDs).
✅ Guaranteed returns
You know your return from day 1.
✅ Flexible tenures
From days to years.
✅ Senior citizen advantage
Extra interest rate offered in many banks.
✅ Loan against FD available
You can borrow against it instead of breaking it.
✅ No market volatility stress
Unlike shares or mutual funds, FD doesn’t swing daily.
FD vs Savings Account vs RD: Which Gives Better Returns?

FD usually gives better returns than a savings account because savings interest is lower.
Savings Account
- Very liquid
- But lower interest
RD (Recurring Deposit)
- Monthly savings habit
- Similar interest rates to FD sometimes
- Good for salary earners
FD (Fixed Deposit)
- Best for lump sum investment
- Higher returns than savings
- Stable and predictable
If your goal is safe growth, FD usually beats savings accounts in returns.
FD for Senior Citizens: Extra Interest and Special Benefits
FD is extremely popular among senior citizens because banks often offer extra interest.
Some banks also provide special schemes. For example, SBI provides additional benefits for senior citizens and even mentions extra benefits for super senior citizens (80+), depending on the product rules.
In general:
- Senior citizens may get 0.25% to 0.75% extra interest
- Monthly interest payout options help as retirement income
This makes FD one of the most preferred tools for regular cashflow.
FD Taxation in India: TDS, Form 15G/15H, and Tax-Saving FD
FD interest is taxable in India under “Income from Other Sources.”
TDS Rules (Important)
Banks may deduct TDS if interest crosses the limit.
As explained in Income Tax guidance under Section 194A, the threshold can differ depending on the payer and category, and senior citizen thresholds can be higher under updated rules.
✅ If your total income is below taxable limit:
- You can submit Form 15G (for non-senior citizens)
- You can submit Form 15H (for senior citizens)
Tax-Saving FD (Section 80C)
- 5-year lock-in
- Eligible for deduction under 80C (up to ₹1.5 lakh limit)
- Interest is still taxable
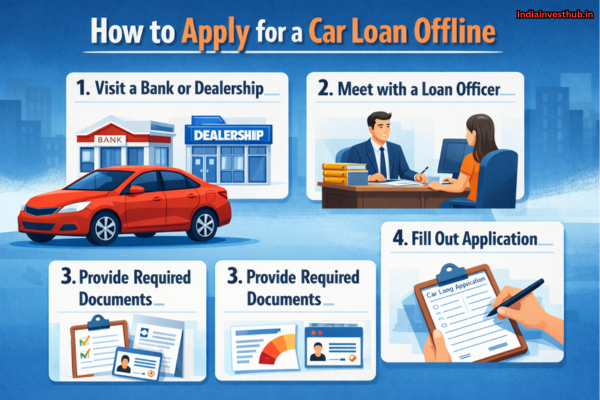
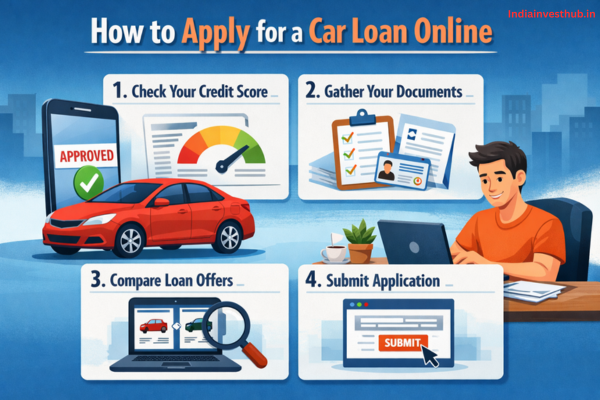
How to Open an FD Online (SBI, HDFC, ICICI, Post Office, etc.)
FD can be opened online easily now:
Bank FD (Online Method)
- Log in to your bank app/netbanking
- Go to “Deposits / Fixed Deposit”
- Enter amount + tenure
- Select interest payout type
- Confirm and create FD
Post Office FD
You can open it through:
- Post office branch
- Some digital channels depending on services
Online FD booking is fast and helps you compare rates instantly before investing.
FAQs — Fixed Deposit
Q1: Is FD safe in India?
👉Yes, FD is considered one of the safest investment options, especially bank FDs and post office FDs.
Q2: Can I break my FD before maturity?
👉Yes, but you may lose some interest as penalty (varies by institution).
Q3: Is FD better than mutual funds?
👉FD is safer and stable, but mutual funds may give higher returns with risk.
Q4: Do senior citizens get higher FD interest rates?
👉Yes, most banks offer extra interest rates for senior citizens.
Q5: Is FD interest taxable?
👉Yes, FD interest is taxable as per income tax rules.
Conclusion:
FD is still one of the smartest options for investors who want guaranteed returns, capital safety, and predictable income without worrying about market ups and downs. Whether you choose a bank FD, post office FD, or even a corporate FD, the key is matching the tenure, interest rate, and tax plan with your goal.
So before you invest, ask yourself honestly—are you choosing FD for safe wealth protection, or do you need higher returns even if it comes with higher risk?